1. Understanding the Importance of WhatsApp Backups
1.1 The Value of Your WhatsApp Data
WhatsApp stores more than casual conversation; it contains personal memories, business communications, and verification codes that often serve as proof of transactions. Each chat thread may hold photos, videos, voice notes, and documents that cannot be recreated once deleted.
- Text messages: record decisions, agreements, and personal milestones.
- Media files: preserve moments captured during trips, events, and celebrations.
- Voice recordings: capture nuanced information that may be lost in written form.
- Documents: contain invoices, contracts, and other legal material exchanged through the app.
- Account authentication data: include two‑factor codes and verification links essential for accessing other services.
Loss of this data disrupts personal narratives, hampers professional workflows, and can compromise security when authentication messages disappear. Restoring the content after accidental deletion or device failure is often impossible without a prior backup.
Consequently, implementing a reliable backup strategy is mandatory for safeguarding these assets. Regularly scheduled backups, encrypted storage, and verification of successful restore points create a safety net that prevents irreversible loss.
1.2 Potential Data Loss Scenarios
Potential data loss with WhatsApp can occur through several distinct mechanisms. Device malfunction, such as hardware failure or operating‑system corruption, may erase local chat databases before they are transferred to a cloud service. Accidental deletion of the application or its storage folder removes all messages, media, and configuration files, leaving no trace on the device. Inadequate backup frequency creates gaps; any messages received after the last successful backup remain vulnerable if the device is lost or damaged. Cloud‑service disruptions, including account suspension, credential loss, or service outages, prevent retrieval of stored archives. Migration between operating systems-Android to iOS or vice versa-often excludes native backup formats, resulting in incomplete transfer. Encryption key loss, whether due to forgotten passcodes, corrupted key files, or third‑party app interference, renders encrypted backups unreadable. Lastly, malware or unauthorized access can corrupt or delete backup files, eliminating recovery options entirely. Recognizing these scenarios is essential for implementing safeguards that protect valuable conversation history.
2. Exploring WhatsApp Backup Options
2.1 Local Backups: A Convenient but Limited Solution
Local backups store chat histories, media, and settings directly on the device’s internal memory or an attached SD card. The process is triggered by WhatsApp’s built‑in “Export chat” function or by enabling the automatic local backup option in the app’s settings. Files are saved in a folder typically named “WhatsApp/Databases” and can be accessed through a file manager or connected to a computer for copying.
Advantages of this approach include immediate availability, zero reliance on external services, and the ability to retrieve data without internet connectivity. Users can create multiple copies, archive them on external drives, or encrypt them for added security.
Limitations are significant:
- Retention period is short; older backups are overwritten after seven days, risking loss of historical data.
- Backups remain tied to a single device; hardware failure, loss, or theft renders the data inaccessible.
- No synchronization across multiple devices; switching phones requires manual transfer of the backup file.
- Absence of cloud redundancy means no automatic off‑site protection against disasters such as fire or water damage.
To mitigate these drawbacks, combine local backups with periodic transfers to cloud storage, external hard drives, or encrypted archives. Establish a routine that copies the latest backup file at least once per week, verifies integrity, and stores it in a separate physical location. This hybrid strategy preserves the convenience of on‑device snapshots while safeguarding against the inherent vulnerabilities of a solely local solution.
2.2 Google Drive/iCloud Backups: Leveraging Cloud Storage
Google Drive (Android) and iCloud (iOS) provide reliable, automated storage for WhatsApp chat histories, media files, and settings. When correctly configured, they eliminate the need for manual export and safeguard data against device loss or damage.
Key actions to maximize cloud backup reliability:
- Link the correct Google account or iCloud ID to WhatsApp before initiating the first backup.
- Enable “Daily” or “Weekly” backup frequency in the app’s settings; avoid “Manual only.”
- Verify sufficient free space in the cloud account; allocate at least twice the estimated size of current WhatsApp data.
- Activate two‑step verification for the cloud service to prevent unauthorized access.
- Periodically test restoration by reinstalling WhatsApp on a secondary device and confirming that recent messages and media appear intact.
- Retain older backups for at least 30 days to protect against accidental deletion; adjust retention policy in the cloud console if needed.
By adhering to these steps, users ensure that WhatsApp information remains continuously protected in the cloud, ready for swift recovery on any compatible device.
2.3 Third-Party Backup Apps: Expanding Your Options
Third‑party backup solutions broaden the range of strategies for preserving WhatsApp conversations, media, and attachments beyond native cloud services. These applications typically aggregate data from the device’s storage, convert it into portable formats, and store it on external destinations such as Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive, or local encrypted archives.
When selecting an auxiliary tool, evaluate the following criteria:
- Compatibility with the device’s operating system and WhatsApp version.
- Encryption standards applied during transfer and at rest.
- Frequency of automatic backups and customizable scheduling.
- Support for selective restoration of individual chats or media groups.
- Transparency of privacy policies and absence of data harvesting.
- Pricing structure, including free tier limitations and subscription costs.
Widely recognized options include:
- Backuptrans Android WhatsApp Transfer - offers direct export to PC, selective chat restoration, and encrypted archive creation.
- iMazing - provides iOS‑focused backup with granular control over chat threads and media, plus secure local storage.
- Dr.Fone - WhatsApp Transfer - integrates cross‑platform migration, scheduled cloud uploads, and password‑protected archives.
Implementing one of these tools alongside the built‑in backup mechanism creates redundancy, reduces reliance on a single service, and safeguards critical communication data against accidental loss or account compromise.
3. Choosing the Right Backup Method for You
3.1 Assessing Your Needs and Preferences
When planning a backup strategy for WhatsApp, begin by identifying the volume and type of data you need to preserve. Large media libraries, frequent chat histories, and critical business conversations each demand different storage solutions and retention periods.
Determine the devices that will hold copies of your data. A primary smartphone, a secondary phone, and a cloud service each have distinct security models and accessibility constraints. Assess whether you require cross‑platform access (e.g., Android to iOS) or if a single‑platform solution suffices.
Evaluate your tolerance for data loss and recovery time. If a few hours of downtime is unacceptable, choose a backup method that offers near‑real‑time synchronization. If occasional delays are tolerable, scheduled backups may reduce storage costs.
Consider privacy and compliance requirements. Encrypted backups, regional data residency, and retention policies must align with personal or organizational regulations.
Key assessment criteria:
- Data size (messages, images, videos, documents)
- Frequency of new content generation
- Desired backup interval (daily, weekly, continuous)
- Preferred storage location (local device, external drive, cloud)
- Security features (encryption, password protection)
- Device ecosystem (Android, iOS, both)
- Regulatory constraints (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.)
By systematically reviewing these factors, you can select a backup configuration that matches your specific usage patterns and risk profile, ensuring that valuable conversations remain recoverable under any circumstance.
3.2 Balancing Convenience, Security, and Storage Space
Balancing ease of use, data protection, and storage efficiency is essential for reliable WhatsApp backups. A backup that is simple to restore may expose sensitive messages if encryption is weak, while strict security measures can complicate recovery on low‑capacity devices. Effective practice requires a measured approach that addresses each factor without compromising the others.
- Automation vs. control: Schedule daily incremental backups to reduce manual effort, but retain the option to trigger a full backup before major changes, such as OS upgrades.
- Encryption strength: Apply end‑to‑end encryption with a strong, user‑managed key. Store the key separately from the backup file to prevent loss while keeping the backup accessible on the primary device.
- Compression: Enable lossless compression to shrink media‑heavy chats, conserving space on cloud services and local drives. Verify that the compression algorithm does not interfere with encryption integrity.
- Retention policy: Keep a rolling window of recent backups (e.g., last 30 days) and archive quarterly snapshots. This limits storage growth while preserving recovery points for critical periods.
- Multi‑location storage: Duplicate encrypted backups to two distinct services (e.g., Google Drive and a personal NAS). Ensure each location respects the same security settings, providing redundancy without excessive storage consumption.
By integrating scheduled incremental backups, robust encryption, selective compression, a clear retention schedule, and diversified storage, users achieve a practical equilibrium. The configuration minimizes manual intervention, safeguards privacy, and prevents unnecessary consumption of storage resources.
4. Implementing Best Practices for WhatsApp Backups
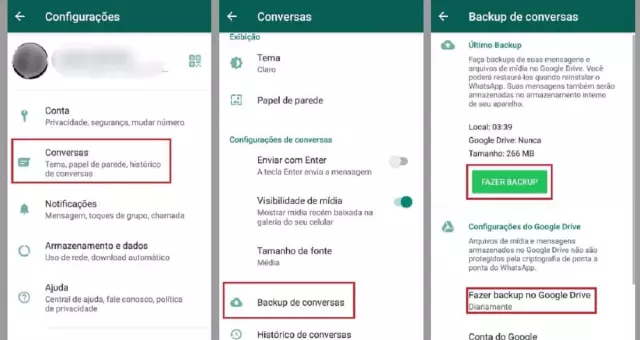
4.1 Setting Up Automatic Backups
To activate automatic backups, open WhatsApp, tap Settings → Chats → Chat backup, then press “Back up to Google Drive” (Android) or “Auto‑Backup” (iOS). Select a backup schedule-daily, weekly, or monthly-according to the volume of messages and available storage. Choose the preferred account for cloud storage, ensure the account has sufficient free space, and confirm that the backup includes both chat history and media files if needed.
Configure network usage to avoid unexpected data charges. For Wi‑Fi‑only backups, enable the “Only over Wi‑Fi” option; otherwise, allow cellular uploads for more frequent backups. Activate end‑to‑end encryption by toggling the “Encrypt backup” switch and recording the generated password in a secure location; without this key, restored data will remain inaccessible.
Set a retention policy to manage storage growth. Periodically delete older backup snapshots from the cloud console, or limit the backup size by deselecting large media categories such as videos or GIFs. Verify the backup status after each scheduled run: the “Last backup” timestamp should reflect the recent operation, and the backup size should align with expectations.
Maintain reliability by:
- Keeping the app updated to the latest version.
- Ensuring the cloud account remains signed in.
- Monitoring available storage on both the device and the cloud service.
- Testing restoration on a secondary device after major updates.
These actions create a self‑sustaining backup cycle that safeguards conversation history and attached files without manual intervention.
4.2 Verifying Backup Completeness
After creating a backup, confirm that the stored data matches the original conversation archive. A mismatch indicates corruption or incomplete transfer, which can lead to loss during restoration.
- Open the backup file (e.g., msgstore.db.crypt12) with a compatible viewer and verify the total message count against the live chat list.
- Compare the file size and modification date with previous backups; a sudden drop suggests missing content.
- Generate a checksum (MD5 or SHA‑256) for the backup file, then recompute it after copying to another device or cloud location; identical values prove integrity.
- Run a test restore on a secondary device or emulator, then inspect a representative sample of chats and media to ensure they render correctly.
- For media files, cross‑check the number of attached images, videos, and documents listed in the backup manifest with the actual files present in the media folder.
If any discrepancy appears, repeat the backup process immediately and repeat the verification steps before discarding the faulty copy. This routine guarantees that every stored conversation and attachment remains fully recoverable.
4.3 Protecting Your Backup Data
Protecting the data stored in your WhatsApp backups requires a layered approach that addresses encryption, access control, storage location, and integrity verification.
First, enable end‑to‑end encryption for cloud backups whenever the service provides it. Encryption keys should be stored outside the backup file, preferably in a password‑protected vault or a hardware security module. If the platform does not support built‑in encryption, encrypt the backup archive with a strong algorithm (AES‑256) before uploading.
Second, restrict access to the backup account. Use a unique, complex password and activate two‑factor authentication. Limit device synchronization to trusted devices only, and regularly review authorized devices in the account settings.
Third, diversify storage locations. Keep a copy in a reputable cloud provider, and maintain an offline version on an encrypted external drive. Offline copies protect against cloud‑service outages, ransomware attacks, or accidental deletions.
Fourth, verify backup integrity on a scheduled basis. Perform the following steps at least monthly:
- Download the latest backup file.
- Decrypt and open the archive to confirm readability.
- Compare file hashes with the original export to detect corruption.
- Restore a small sample of messages or media to ensure the restoration process works.
Finally, retain backup logs. Record the date, storage medium, encryption method, and verification results. Logs enable quick identification of outdated or compromised backups and support compliance with data‑retention policies.
4.4 Regularly Reviewing and Updating Your Backup Settings
Regularly inspecting your WhatsApp backup configuration prevents silent failures that could compromise chat history, media, and documents. Settings that were appropriate months ago may become outdated after OS updates, storage policy changes, or new features introduced by the platform.
Key actions for a systematic review:
- Open the app’s backup menu at least once every quarter. Verify the selected drive (Google Drive, iCloud, or local storage) matches your current device and account.
- Confirm the backup frequency (daily, weekly, or manual) aligns with your usage intensity. Increase frequency if you exchange high‑value media or sensitive information.
- Check encryption status. Ensure end‑to‑end encrypted backups are enabled, and note the recovery key location.
- Review storage quotas on the cloud service. Free tiers may fill quickly, causing new backups to be skipped.
- Test restoration by downloading the latest backup to a secondary device. Successful restoration confirms integrity and accessibility.
After adjustments, document the chosen parameters in a secure note. Schedule the next audit in the calendar to maintain consistency and avoid accidental data loss.
5. Restoring WhatsApp from a Backup
5.1 Understanding the Restoration Process
Understanding the restoration process is essential for preserving chat history, media, and settings after a backup has been created. The procedure begins with locating the most recent backup file, which may reside on iCloud, Google Drive, or local storage, depending on the operating system. Ensure the backup matches the WhatsApp version currently installed; mismatched versions can cause incomplete restores or errors.
The restoration workflow follows these steps:
- Install WhatsApp on the target device and verify the phone number through the standard verification code.
- When prompted, grant access to the storage location containing the backup file.
- Confirm the backup’s timestamp to select the desired restore point.
- Allow the app to download (cloud) or copy (local) the backup data.
- Wait for the decryption process to complete; encrypted backups require the original password or key.
- Review the restored chat list and media folders to confirm integrity.
Key considerations:
- Encryption: Encrypted backups cannot be restored without the correct passphrase; loss of the passphrase renders the data unrecoverable.
- Device compatibility: Restoring from Android to iOS (or vice versa) is unsupported; data must remain within the same platform ecosystem.
- Storage space: Sufficient free space on the device is mandatory; insufficient space aborts the process and may leave partial data.
- Network reliability: A stable connection prevents interruptions during cloud download, reducing the risk of corrupted files.
After completion, initiate a fresh backup to capture the newly restored state, ensuring that future recovery attempts start from a verified baseline. Regularly testing the restoration process-by performing a trial restore on a secondary device-confirms that backups remain functional and that recovery steps are well understood.
5.2 Troubleshooting Common Backup Restoration Issues
When a WhatsApp backup fails to restore, the problem typically falls into one of several categories: corrupted file, version mismatch, insufficient storage, or account authentication error. Identify the symptom first, then apply the corresponding remedy.
- Corrupted backup file - Verify the integrity of the backup by checking its size in Google Drive or iCloud. If the file appears unusually small or incomplete, delete it and create a new backup from the current chat history.
- Version mismatch - Ensure the app version on the device matches the version used to create the backup. Update WhatsApp to the latest release before attempting restoration.
- Insufficient storage - Confirm that the device has enough free space to accommodate the restored data. Clear cache, uninstall unused apps, or move media to external storage before proceeding.
- Authentication error - Re‑enter the phone number linked to the backup and verify the SMS or email code. If two‑factor authentication is enabled on the associated Google or Apple account, confirm that the correct credentials are supplied.
If the above steps do not resolve the issue, perform a manual extraction of the backup file. Download the encrypted file from the cloud service, use a reputable decryption tool to convert it to a readable format, then import the resulting database into WhatsApp via the “Restore from local backup” option. Finally, document the error code displayed in the app log and consult official support resources for any code‑specific guidance.